Presentation
The Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement set a global action plan to limit global warming below 2°C above pre-industrial level, with the aim to significantly reduce the risks linked to climate change by limiting the increase of temperatures to 1.5°C by 2100. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it implies reaching net zero CO2 emissions globally in 2050.
The potential of circular economy
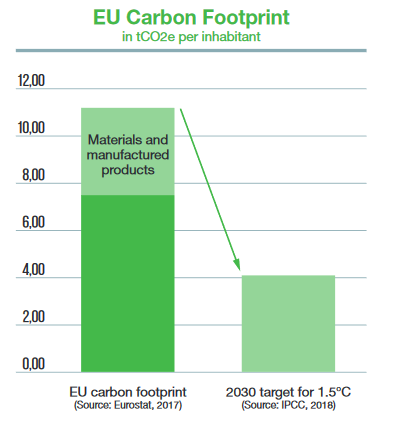 To reach carbon neutrality in 2050, the carbon footprint of EU citizens must decrease from about 11 tCO2e to 4 tCO2e per inhabitant in 2030;
To reach carbon neutrality in 2050, the carbon footprint of EU citizens must decrease from about 11 tCO2e to 4 tCO2e per inhabitant in 2030;- According to different sources, the impact of food and material production accounts for 33% to 45% of the European carbon footprint;
- Circular economy has a tremendous potential to mitigate the impact of products, by preventing waste generation, extending the lifetime of products, and closing the loops of materials.
It is possible for European cities and regions to reduce the EU carbon footprint of several key sectors by implementing ambitious, yet feasible actions. These sectors are: food, construction, textiles, electronic and electrical equipment, plastic. However, these key sectors might be different from one territory to another, depending on the current practices, consumption patterns, and local context.
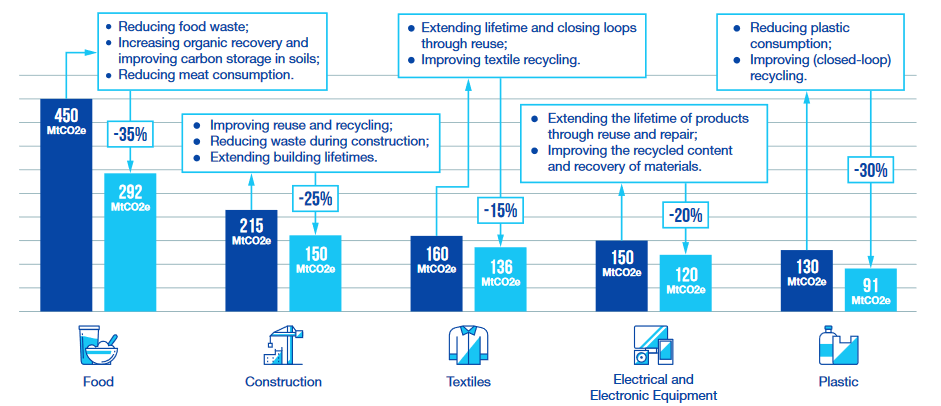
It is also important to note that waste management has a rather limited direct impact on carbon emission. Waste-centred approaches are too limited to effectively tackle the carbon footprint of material resources. Circular economy strategies should therefore focus more on production and consumption, and on the production of relevant secondary raw materials to decrease the extraction of virgin materials.
ACR+'s 25th anniversary, making the link between circular economy and climate mitigation
For more than 25 years, ACR+ has been supporting cities and regions in their transition towards a circular economy by promoting a sustainable resource management, encouraging the exchange of good practices and experiences between members, and sharing technical and policy information. The network strongly advocates for the key role of cities and regions in the circular economy.
To celebrate its anniversary and push further its message, ACR+ was determined make the link between circular economy and climate mitigation. For that, it was necessary to show that cities and regions are crucial players to reduce the carbon footprint of several key sectors by implementing ambitious yet feasible actions to prevent losses and waste, extend the lifetime of products, and close the loops of materials.
This is how the More Circularity, Less Carbon campaign was born.
The Campaign
The campaign will run from November 2019 to November 2025, seeing ACR+ members taking steps at their level to reduce the carbon emissions linked with local resource management by 25% by 2025.
A call to action
Governments are setting ambitious strategies. However, to reach the commitments taken fast, and effective actions are necessary at all levels. ACR+ and its members are ready to act at their local level.
Together, they will contribute to the global fight against climate change while taking into account the local carbon footprint of material resources and waste. They will build on their key role as public authorities, mobilising local stakeholders and citizens, to drive waste prevention and management and advance the circular economy throughout their jurisdictions in order to reduce carbon impacts. Their goal?
Reduce the emissions linked with local resource management by 25% by 2025
Activities
Behind its ambitious goal, the campaign takes into account the diversity of contexts, scope of actions and policy instruments across participating authorities. Participating members will assess their carbon footprint, set their own action plans, monitor the results, and put in common their good practices and findings, under the coordination of ACR+ secretariat. They will benefit from the following activities:
- Exchange good practices;
- Conduct cross analysis with annual reports;
- Improve and mainstream the inclusion of carbon consideration in local circular economy policies;
- Benefit from tools and methodologies open to all, with the assistance of ACR+ Secretariat for the collection of data and the analysis of results.
The Carbon Metric International, toward climate-oriented strategies
To go beyond weight-based waste measurement a specific tool will be developed: the Carbon Metric International. This will be adapted from the Scottish Carbon Metric, which has been used by Zero Waste Scotland since 2011 to measure the whole life carbon impacts of Scotland’s waste, regardless of where in the world they occur. It includes the emissions from resource extraction and manufacturing of the products that turned into waste. This type of carbon accounting gives a more complete picture of the impacts of products, allowing decision makers to prioritise their efforts for maximum carbon savings.